Navigating the ocean of dietary choices, one often overlooks the simplest yet most vital element—water. As the quintessential zero-calorie beverage, it not only satisfies thirst but also serves critical roles in our bodies. From aiding metabolism to ensuring proper digestion, water is the cornerstone of any balanced hydration guide. When paired with food, a water diet emerges as a powerful ally for those seeking healthy water consumption and overall wellness. The amalgamation of hydrating fluids and water-rich foods equips individuals with the means to maintain bodily functions optimally while supporting a journey towards sustainable health goals.
Key Takeaways
- Understand water’s indispensable role in a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
- Discover how a water diet with food supports essential bodily functions and metabolism.
- Grasp the significance of water as a calorie-free option in your hydration routine.
- Learn how to integrate optimal hydration practices into daily water consumption patterns.
- Acknowledge the impact of combining water consumption with nutrient-rich foods.
- Recognize the personal nature of hydration needs and how water contributes to your health.
- Educate on the essentials of a balanced hydration guide for vitality and well-being.
Understanding Water’s Role in a Healthy Diet
Water is more than a thirst quencher—it’s a fundamental component of a hydration diet and plays a critical role in health. While often undervalued, the liquid sustains life and supports a plethora of bodily functions. Balancing water intake is a nuanced art, taking into consideration daily fluid intake recommendations, individual needs, and lifestyle factors. Beginning to chart the waters of optimal hydration opens the door to enhanced well-being and health.
Essential Functions of Water in the Body
Every sip of water taken is a step toward maintaining the body’s complex symphony of processes. It restores fluids lost through metabolism, breath, perspiration, and waste. Further, as the body’s primary coolant, water averts overheating, lubricates joints, and nourishes the skin. For those adhering to a hydration diet, understanding water’s integral role in health is the key to harnessing its benefits fully.
Guidelines for Daily Water Intake
How much water should you include in your hydration diet? The National Academy of Medicine steers away from the one-size-fits-all mantra of “8 glasses a day,” offering more personalized daily fluid intake recommendations. Their research underlines approximately 13 cups for men and 9 cups for women as a baseline, factoring in variations due to physical activity and environmental exposure, to ensure a body is well-hydrated.
| Category | Daily Adequate Intake |
|---|---|
| Men (19+ years) | 13 cups (104 ounces) |
| Women (19+ years) | 9 cups (72 ounces) |
| Pregnant Women | 10 cups (80 ounces) |
| Breastfeeding Women | 13 cups (104 ounces) |
Factors Affecting Individual Hydration Needs
Why the variance in fluid intake recommendations? Hydration needs are not static; they are influenced by more than a pattern of daily habits. Fever, exercise, and environmental conditions, for instance, can escalate fluid requirements. When discussing a hydration diet, one must consider alcohol consumption which may suppress the anti-diuretic hormone, subsequently flushing out water from the body. Caffeine, on the other hand, could increase urination without contributing to dehydration. Further, water-rich foods like fruits and veggies add to one’s fluid intake—up to 20%. Urine’s color and volume can also serve as a hydration barometer. These nuances are vital in optimizing one’s water’s role in health, ensuring each individual’s daily fluid intake recommendations are met effectively.
The Impact of Water Diet with Food on Weight Loss
In the realm of health and well-being, drinking water for weight loss has emerged as a well-documented ally. Delving into the intricacies of weight management, research pinpoints the significant role water plays when combined with a mindful eating regime. It’s not simply about the consumption of water but the strategic incorporation of it with food that can tip the scales in favor of healthy weight loss.
Initiating a meal with a glass of water is more than a ritual; it is a science-backed strategy for fostering satiety. By filling the stomach before eating, water can naturally curb appetite, leading to a reduction in calorie consumption. This practice is a cornerstone of a water diet, where hydrating adequately before meals can preclude overindulgence, aligning eating habits with the objectives of weight reduction.
The avoidance of high-calorie beverages in favor of water is another pillar in the architecture of weight loss. Sugary sodas and assorted drinks, often dense with unnecessary calories, find a formidable replacement in water—a beverage devoid of calories but abundant in benefits. By making this substitution, individuals are not only able to reduce their caloric intake significantly but also contribute positively to their overall health.
Water fasting for health, an approach entailing short-term abstinence from all drinks except water, is viewed by some as a method to detoxify and initiate metabolic processes conducive to weight loss. Yet, this practice should be approached with caution and understanding of one’s individual health needs, ideally under professional guidance.
Hydration extends beyond the act of drinking water. It encompasses the metabolic processes that underly weight management. Adequate hydration aids in the maintenance of a continuous calorie-burning mechanism. It is a silent yet critical phenomenon that supports the body’s innate capacity to manage weight effectively when coupled with a balanced diet.
Proper hydration is an essential component of a balanced diet and has a direct impact on weight management and metabolic health.
- Drinking water assists in reducing overall calorie intake.
- Replacing sugary beverages with water is key to cutting excess calories.
- Hydration supports metabolic function, crucial for calorie burning and weight loss.
- Integrating water appropriately with meals can aid in achieving satiety.
The synergistic effect of a water diet with food reveals a practical, healthful approach to navigating the challenging waters of weight loss. Thus, proper water intake becomes an indispensable tactic in the diverse arsenal available for those pursuing a healthier, more balanced weight management journey.
Incorporating Water-Rich Foods for Optimal Hydration
The quest for staying adequately hydrated extends beyond the realm of drinking water. In the pursuit of a balanced diet, integrating water-rich foods into your meal plan offers a plethora of benefits for your overall health. As we explore the advantages of such foods, let’s delve into why including them in your diet provides more than just hydration – they offer nutritional bonuses and are essential elements of any health-conscious individual’s meal planning.
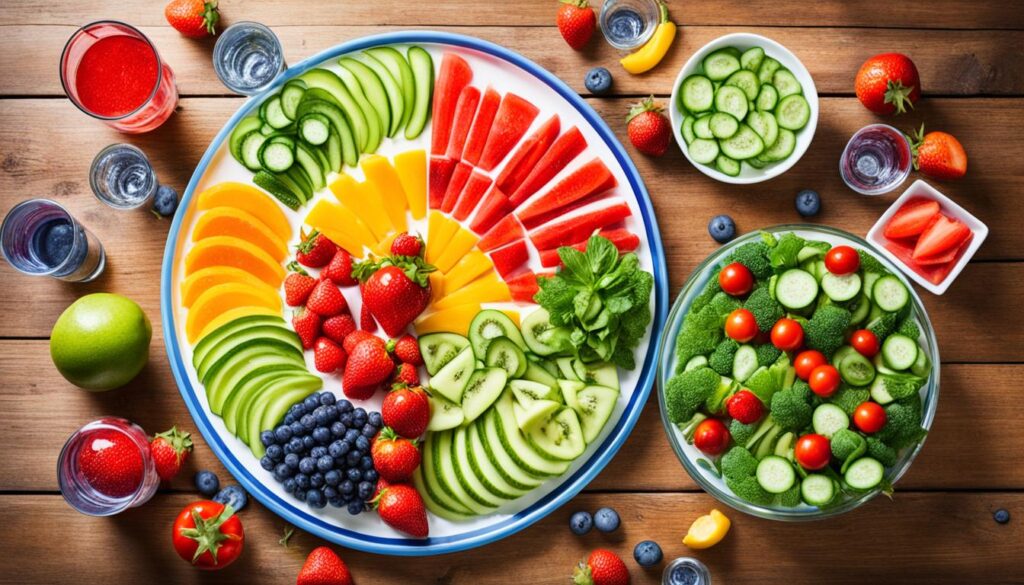

Benefits of Water in Diet Beyond Drinking
Water’s omnipresence in our daily intake is not solely due to the glasses we drink. Roughly 20% of our hydration comes from the foods we consume, particularly those abundant in water content. Including these water-rich foods in your diet aids in a variety of ways – they enhance satiety, helping control overeating, promote a healthy digestive system, and offer crucial nutrients and fiber. Moreover, the integration of such foods contributes to a more comprehensive hydration strategy, emphasizing the benefits of water in diet, beyond what we typically think of as hydration.
Top Water-Rich Foods to Include in Your Meals
When designing a meal plan with water, it’s important to highlight particular foods known for their high water content. These ingredients can effortlessly increase your water intake without the need to constantly refill your water bottle.
- Lettuce (especially iceberg) stands out in the leafy greens category, with a water content that can reach up to 96%.
- Cucumbers, with their cool, crisp texture, boast a water content of approximately 95%, making them a perfect hydrating snack.
- Tomatoes enrich dishes with their flavor and carry a water content of around 94%.
- Celery is not only low in calories but also packed with water at about 95%, alongside essential minerals like potassium.
- Watermelon, a summertime favorite, is made up of 92% water and also provides vitamins C and A, as well as antioxidants.
- Berries, including strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries, are not only delicious and fiber-rich but also have high water content, with strawberries at the top at around 91%.
- Oranges, offering a sweet citrus burst, are composed of about 87% water and provide a valuable dose of vitamin C.
Integrating these water-rich foods into a balanced diet ensures hydration and delivers vital vitamins and minerals, supporting overall wellness and leading to more effective water consumption.
Adapting Your Fluid Intake During Physical Activity and Environmental Changes
As our bodies are subjected to various physical and environmental pressures, there’s a concurrent need for fluid intake adjustments to maintain a balanced diet with water. Staying duly hydrated during exercise is of paramount importance, particularly as the intensity and temperature of our activities vary. It’s about tuning into our body’s signals and replenishing its reserves with the right amount of liquids to sustain peak performance and health.
Engaging in physical activity, whether it’s a brisk walk or a marathon, expends energy and water primarily through sweat. This loss needs to be countered with increased water intake—ideally before, during, and after the activity—to ensure recovery and maintain good hydration levels. This method of proactive replenishment is key to any program aimed at a balanced diet with water. The following table illustrates some recommended fluid intake adjustments for various exercise scenarios, emphasizing the necessity to stay adequately hydrated during exercise.
| Activity Intensity | Pre-Exercise | During Exercise | Post-Exercise |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Intensity ( | At least 2 cups (16 oz) | 5-10 oz every 20 mins | Recover with 2-3 cups (16-24 oz) |
| Moderate Intensity (1-3 hours) | 2-3 cups (16-24 oz) | 7-10 oz every 10-20 mins | 3-4 cups (24-32 oz) or more based on sweat loss |
| High Intensity or Long Duration (> 3 hours) | 3-4 cups (24-32 oz) | 10-12 oz every 15-30 mins | Replenish based on sweat loss. Aim for 16-24 oz per pound lost |
In addition to the rigors of exercise, environmental factors such as heat, humidity, and altitude can demand heightened attention to water intake. The body’s need for water escalates as temperatures soar, underscoring the importance of hydrating during exercise. Similarly, higher altitudes may decrease humidity and increase breathing rates, which can escalate fluid loss. For these reasons, adjusting fluid intake is critical to prevent dehydration and maintain a balanced diet with water.
Illness, stress, or significant life events, such as pregnancy, also bring forth unique hydration requirements. During these times, incremental water intake can aid in recovery, comfort, and overall health maintenance. Monitoring the body’s responses under these conditions—like thirst, urine color, and frequency—is a practical approach to ensuring that you’re aligning hydration with need.
Ultimately, staying attuned to your body’s prompts and the external environment will foster optimal hydration practices. Fluid intake is not merely a static figure but a dynamic requirement that shifts with circumstances. When we adhere to this concept, the principles of a balanced diet with water are upheld, guaranteeing our bodies operate at their finest, whatever the challenge may be.
Conclusion
In the journey towards achieving a state of health and wellness, healthy water consumption plays a pivotal role. This balanced hydration guide has explored the multifaceted water diet with food benefits, demonstrating that, indeed, the essence of life flows through every glass, cup, and bite. Integrating a diet rich in water and water-laden foods becomes a harmonious blend, optimizing the body’s myriad functions and fortifying its resilience against daily challenges.
As detailed throughout the guide, the strategic combination of water intake with food not only supports weight management but also encapsulates personalized hydration needs. Whether through physical exertion or the sways of the environment, recognizing and adapting to our body’s fluid requirements is paramount. The benefit blooms in a balanced hydration guide that transcends mere sustenance, offering a blueprint for vivacity and long-term health.
Embracing the principles laid out in this series ensures that one is equipped to craft a hydration-infused lifestyle, marked by judicious and enjoyable water practices. By advocating for a water diet with food, we unlock the secrets to a more vibrant and refreshed existence where water becomes the unsung hero, working tirelessly to uplift our being in every subtle sip and satisfying crunch.